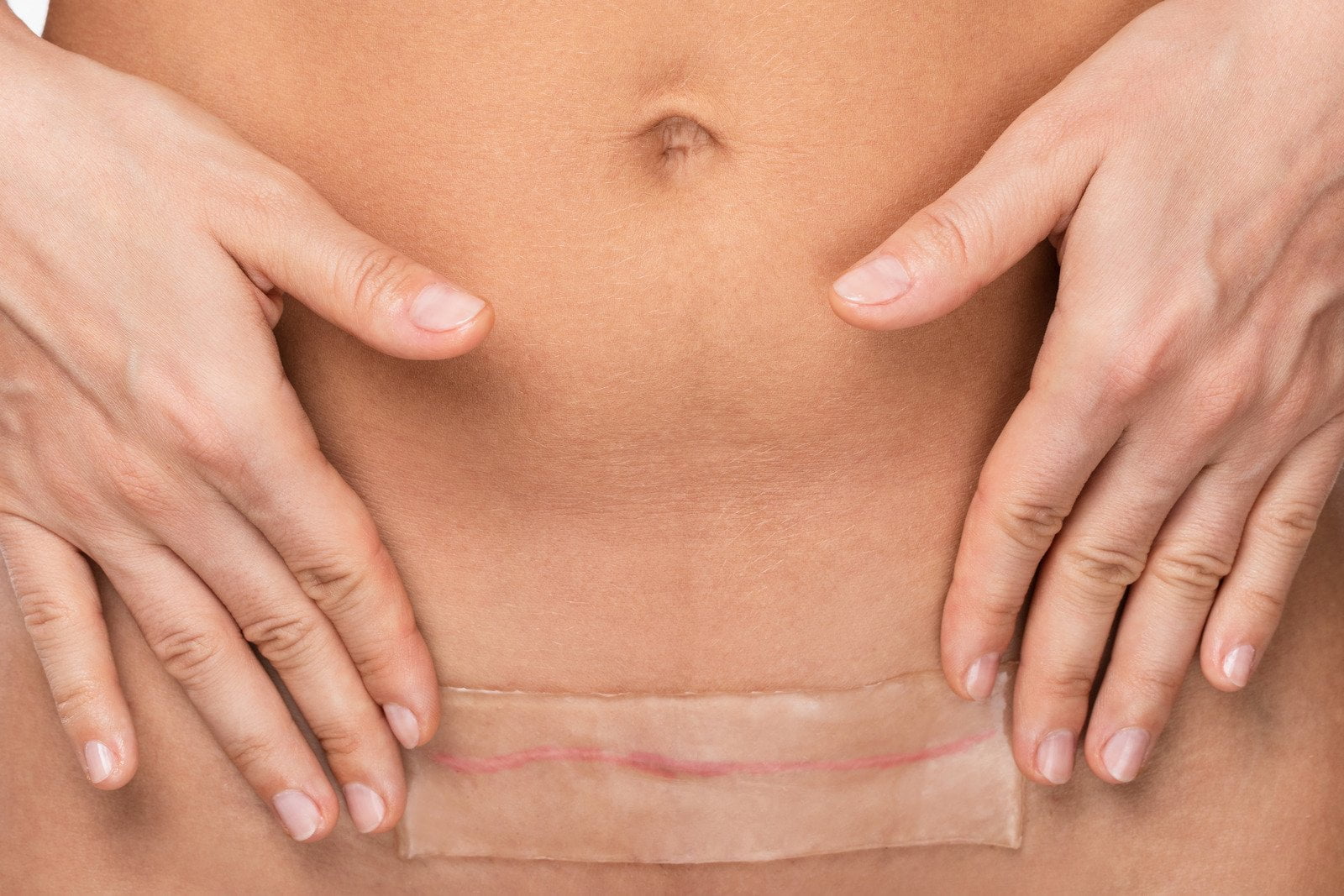
How does silicone help scars? Scars are a natural part of the body’s healing process but can often be aesthetically unpleasing or cause discomfort. Silicone has become a popular treatment for various types of scars. But what exactly does silicone do for scars? This article explores the science behind silicone’s effectiveness in scar treatment.
The Science of Scarring
Scarring is a complex biological process that occurs as a response to injury or surgery. It’s the body’s natural way of healing and replacing lost or damaged skin. However, the process can lead to various types of scars, each with unique characteristics and challenges.
Phases of Scar Formation
1. Inflammatory Phase
- Immediate Response: The body’s immediate response to an injury is to stop bleeding through blood clotting.
- Inflammation: White blood cells are sent to the injury site to fight infection, leading to redness and swelling.
2. Proliferative Phase
- Collagen Production: Fibroblasts produce collagen, a protein that forms the foundation of scar tissue.
- New Blood Vessels: The formation of new blood vessels helps supply nutrients to the healing tissue.
- Wound Contraction: The wound edges pull together, reducing the size of the wound.
3. Maturation Phase
- Collagen Remodeling: Collagen fibers reorganize, and the scar softens and flattens.
- Scar Maturation: The scar becomes paler and less noticeable over time, which can take months or even years.
How Silicone Works on Scars
1. Hydration
Hydration is crucial for the skin’s overall health and is vital in scar healing. Maintaining optimal moisture levels in scar tissue can significantly influence a scar’s appearance, texture, and comfort.
The Importance of Hydration
- Softening Scar Tissue
- Texture Improvement: Hydrated scar tissue becomes softer and more pliable, reducing the stiffness often associated with scars.
- Appearance Enhancement: Proper hydration can make scars less noticeable by improving color and texture alignment with the surrounding skin.
- Promoting Collagen Synthesis
- Balanced Production: Hydration helps normalize collagen synthesis, preventing overproduction that leads to raised scars.
- Improved Organization: Moisture aids in aligning collagen fibers, contributing to a smoother appearance.
- Reducing Itchiness and Discomfort
- Soothing Effect: Hydrated scars are less likely to become itchy or cause discomfort, enhancing the overall healing experience.
Silicone and Hydration
Silicone treatments are known for their ability to provide hydration to scar tissue.
- Moisture Barrier
- Locking in Moisture: Silicone creates a semi-occlusive barrier that locks in moisture, maintaining an optimal hydration level in the scar tissue.
- Preventing overdrying: Silicone seals in moisture, preventing the scar from drying out, which can lead to cracking or increased visibility.
- Enhancing Treatment Effectiveness
- Complementary to Other Treatments: Silicone’s hydration can enhance the effectiveness of other scar treatments, such as pressure therapy or corticosteroid injections.
- Ease of Use
- Convenient Application: Silicone is easy to apply and can be used on various body parts, making hydration maintenance simple and convenient.
2. Occlusion
Occlusion refers to creating a barrier or seal that prevents moisture loss and protects the underlying tissue. In scar healing, occlusion is vital in maintaining a controlled environment that fosters optimal healing conditions.
The Role of Occlusion
- Moisture Retention
- Preventing Dehydration: By creating a barrier, occlusion helps retain moisture within the scar tissue, preventing dehydration that can lead to dryness, cracking, or increased visibility.
- Enhancing Hydration: The occlusive barrier helps maintain a moist environment, promoting hydration, essential for softening scar tissue and improving its appearance.
- Protection from External Factors
- Barrier Against Irritants: Occlusion protects the scar from external irritants such as dirt, bacteria, and environmental factors that can interfere with healing.
- Reduction of Itchiness and Discomfort: By shielding the scar from external stimuli, occlusion can reduce itchiness and discomfort often associated with healing scars.
- Controlled Healing Environment
- Temperature Regulation: An occlusive barrier helps maintain a stable temperature at the scar site, aiding blood flow regulation and reducing inflammation.
- Enhanced Medication Absorption: Occlusion can enhance the absorption of topical medications or treatments, making them more effective.
Silicone and Occlusion
Silicone treatments are mainly known for their occlusive properties.
- Creating a Semi-Occlusive Barrier
- Flexible Seal: Silicone forms a flexible, breathable barrier over the scar, allowing necessary oxygen exchange while retaining moisture.
- Complementing Other Treatments
- Synergy with Other Therapies: Silicone’s occlusive properties can complement other scar treatments, such as pressure therapy or corticosteroid injections, enhancing their effectiveness.
3. Temperature Regulation
Temperature regulation refers to maintaining an optimal temperature at a wound or scar site. This aspect of healing is often overlooked but plays a crucial role in the body’s ability to repair itself efficiently. The right temperature can influence various factors, including blood flow, inflammation, and the overall healing environment.
The Importance of Temperature Regulation
- Blood Flow Regulation
- Optimal Circulation: Maintaining the correct temperature ensures optimal blood flow to the scar site, providing essential nutrients and oxygen that aid healing.
- Preventing Excessive Heat: Excessive heat can dilate blood vessels, leading to increased swelling and potentially slowing the healing process.
- Inflammation Control
- Reducing Inflammation: Controlled temperature helps reduce inflammation, a natural response to injury that, if prolonged, can lead to complications or excessive scarring.
- Balancing Immune Response: Temperature regulation aids in balancing the immune response, preventing overreaction that can cause hypertrophic or keloid scars.
- Enhancing Cellular Activity
- Stimulating Cell Proliferation: The right temperature stimulates cell proliferation, including fibroblasts responsible for collagen production.
- Promoting Collagen Remodeling: Controlled temperature aids in collagen remodeling, leading to a more organized and aesthetically pleasing scar.
Silicone and Temperature Regulation
Silicone treatments contribute to temperature regulation in scar healing.
- Creating a Controlled Environment
- Insulating Effect: Silicone provides a gentle insulating effect, maintaining a stable temperature at the scar site.
- Preventing Rapid Temperature Changes: By creating a barrier, silicone prevents rapid temperature changes that can disrupt healing.
- Complementing Other Treatments
- Enhancing Other Therapies: Silicone’s temperature regulation can enhance the effectiveness of other scar treatments, such as hydration or pressure therapy.
Effectiveness and Safety
Silicone treatments have become a popular and widely accepted method for treating various scar types. Understanding their effectiveness and safety is crucial for healthcare providers and individuals seeking scar treatment.
Effectiveness
- Proven Efficacy in Various Scars
- Types of Scars: Silicone is effective in treating hypertrophic scars, keloid scars, surgical scars, and burn scars.
- Clinical Studies: Numerous clinical studies and systematic reviews have demonstrated the efficacy of silicone in reducing scar height, redness, and stiffness.
- Mechanisms of Action
- Hydration: Silicone locks in moisture, softening the scar tissue.
- Occlusion: It creates a barrier that protects the scar from external factors.
- Temperature Regulation: Silicone helps maintain an optimal temperature at the scar site, aiding blood flow regulation and reducing inflammation.
- Complementary to Other Treatments
- Combined Therapies: Silicone can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments, such as laser therapy, corticosteroid injections, or pressure therapy.
Safety
- Low Risk of Side Effects
- Tolerability: Silicone treatments are generally well-tolerated, with minimal risk of side effects.
- Skin Reactions: Rarely, some individuals may experience minor skin irritation or allergic reactions. Proper application and following instructions can minimize these risks.
- Non-Invasive Treatment
- Ease of Use: Silicone is non-invasive and easily applied at home.
- Suitable for Sensitive Areas: Silicone is gentle enough to be used on sensitive or exposed areas like the face.
- Long-Term Safety
- Prolonged Use: Silicone treatments can be used for an extended period without significant concerns, making them suitable for long-term scar management.
Conclusion
Silicone plays a multifaceted role in scar management, offering hydration, occlusion, and temperature regulation. Its versatility in the form of gels makes it suitable for various scar types and body parts.
By understanding the underlying mechanisms of silicone’s action on scars, individuals can make informed decisions about their scar management and work towards achieving smoother, less noticeable scars.
-
Product on sale
 Scarless Silicone GelOriginal price was: $ 43.00.$ 35.00Current price is: $ 35.00.
Scarless Silicone GelOriginal price was: $ 43.00.$ 35.00Current price is: $ 35.00.